What You Need to Know About BMC Molds
Aug. 14, 2025
What Are BMC Molds?
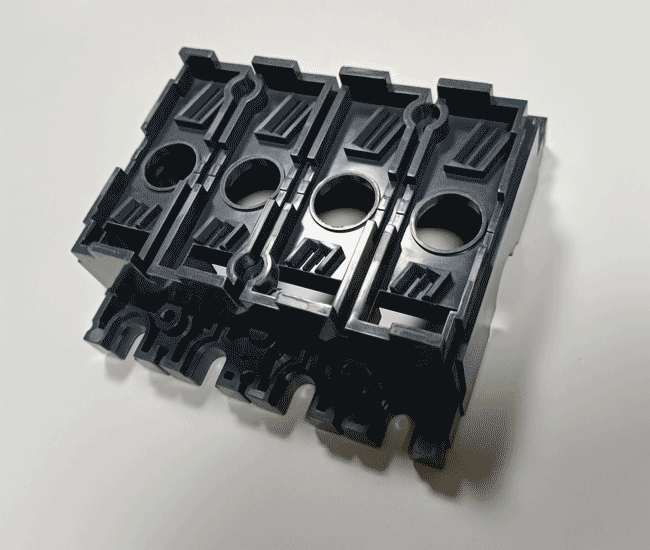
BMC molds are specialized tools used to shape Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) into finished parts. BMC is a thermosetting plastic material made of unsaturated polyester resin, glass fibers, fillers, and additives. These molds are designed to withstand high pressure and temperature, enabling the creation of strong, heat-resistant, and dimensionally stable components. They are commonly made from hardened steel to ensure durability and precision.
BMC Molding Process
The BMC molding process typically follows these steps:
Material Preparation – BMC material, in a dough-like form, is pre-measured to match the mold cavity requirements.
Mold Loading – The compound is placed into the mold cavity.
Compression or Injection – The mold closes, and the material is either compressed or injected into shape under high pressure and heat.
Curing – Heat triggers a chemical reaction that hardens the material permanently.
Demolding – Once cured, the mold opens, and the finished part is removed.
Trimming and Finishing – Any excess material is trimmed, and surface finishing is applied if required.
BMC Molding Applications
BMC molding is widely used across industries because of its excellent mechanical and thermal properties. Common applications include:
Automotive parts – Headlamp reflectors, electrical housings, and under-the-hood components.
Electrical industry – Switchgear components, connectors, and insulators.
Appliances – Handles, housings, and high-heat resistant parts.
Construction – Water meter housings, bathroom fittings, and panels.
How to Design BMC Molds
Designing BMC molds requires careful attention to material behavior and production requirements:
Material Flow Analysis – Ensure smooth filling of cavities without air entrapment.
Draft Angles – Include proper draft angles to make demolding easier.
Venting – Adequate vents prevent air pockets and improve surface finish.
Cavity Layout – Optimize for cycle time, part strength, and minimal waste.
Temperature Control – Integrated heating systems for uniform curing.
BMC Molding Advantages
BMC molding offers multiple benefits over other molding methods:
High strength-to-weight ratio – Ideal for lightweight yet strong components.
Excellent heat resistance – Suitable for high-temperature environments.
Electrical insulation – Non-conductive properties make it perfect for electrical applications.
Corrosion resistance – Withstands moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure.
Complex shape capability – Can produce detailed parts with fine features.
Cost of BMC Molds
The cost of BMC molds depends on factors such as:
Mold complexity – Multi-cavity or intricate designs increase tooling expenses.
Material choice – High-grade steel costs more but offers longer lifespan.
Production volume – Larger runs justify higher initial mold costs through per-part savings.
Customization level – Special surface textures or advanced cooling systems add to the price.
While the initial investment can be high, the durability and efficiency of BMC molds often lead to long-term cost savings, especially for high-volume manufacturing.
270
0
0


Comments
All Comments (0)